Energy generation dependent on supply – i.e. electricity production is dependent on the weather, it does not depend on the demand or the market price (e.g. wind power and photovoltaics) – has an ever increasing influence on the energy market. Especially the flexibility on the demand side is therefore an important success factor for securing our energy system in the long-term. Particularly power-intensive processes in the industry have the potential to profit economically from this.
The goal of the FlexEuro project is the development of methods and prototypes, which can be used for decisions on marketing flexibility in power consumption. To this end, we develop quantitative models and algorithms with a focus on the operational marketing of flexibility together with our project partners. In the network we work as Fraunhofer ITWM together with the University of Duisberg-Essen and two companies from stochastic optimization and industry.
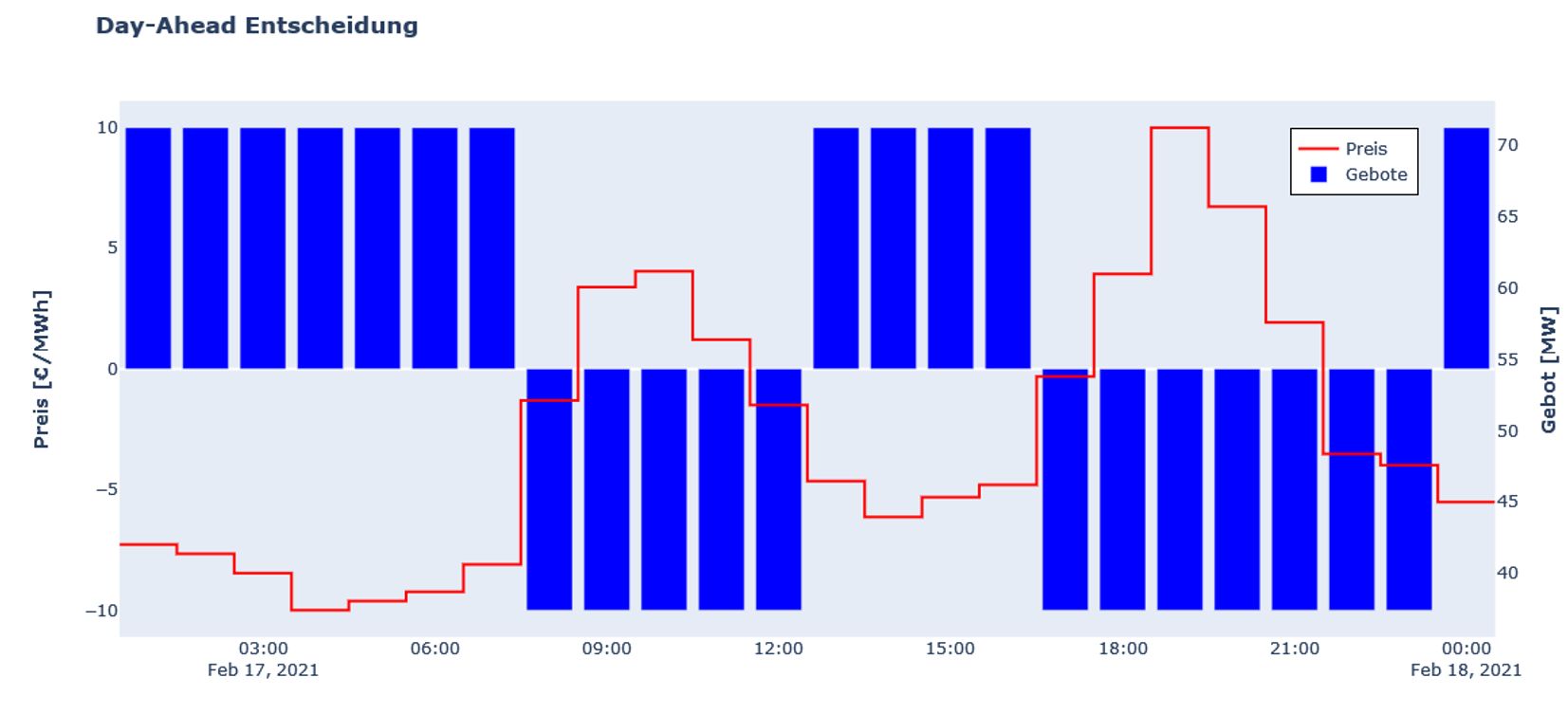
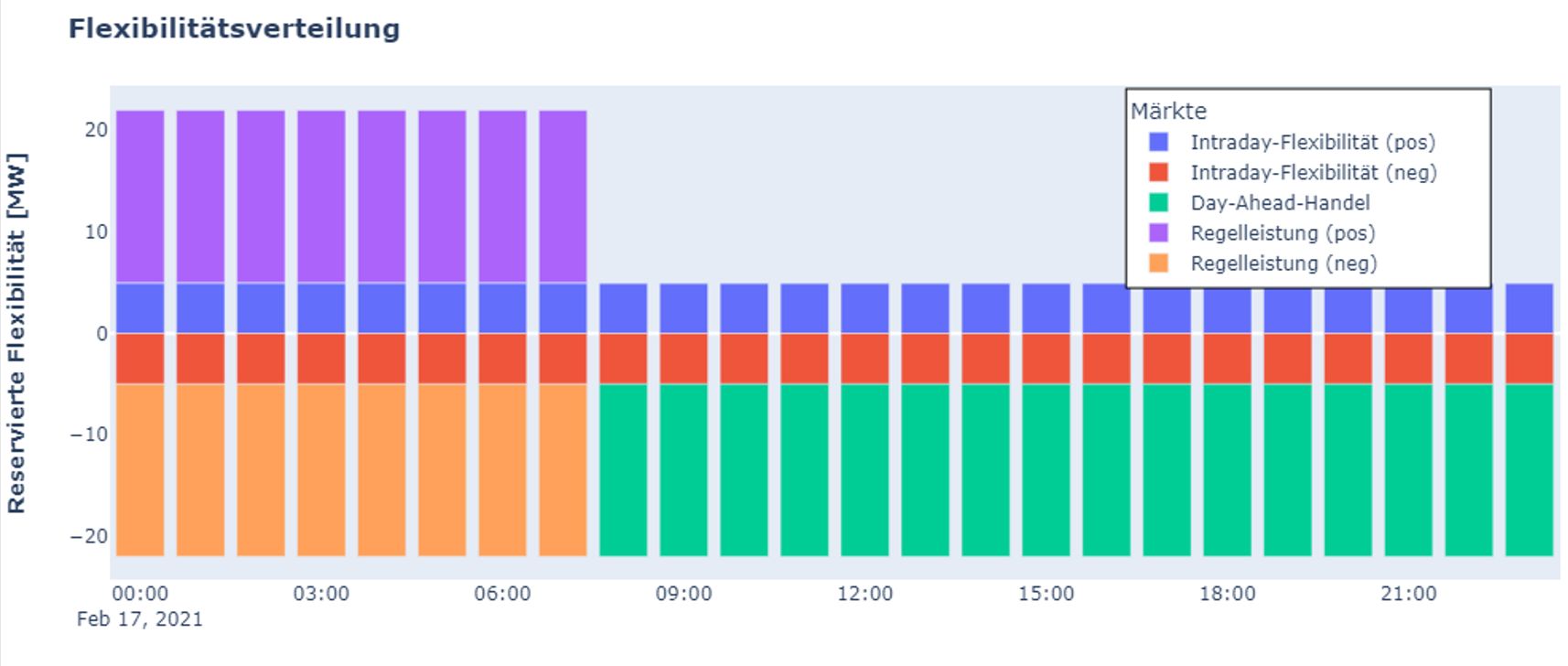
Short-Term Marketing Options
The short-term marketing options for flexibility considered in the project are:
- Reserve power markets: The reserve power guarantees the supply in case of unforeseen events in the power grid.
- Day-ahead Auction: Trading of electricity for the following day, which takes place on EPEX Spot in Paris (Spot Market of the European Power Exchange), on EXAA in Vienna (Energy Exchange Austria) or in OTC (Over-the-Counter Trading) via OTC contracts.
- Intraday market: Intraday trading of electricity takes place both on EPEX Spot and OTC trading, i.e. over-the-counter contracts between electricity buyers and sellers. It refers to the continuous buying and selling of electricity that is delivered on the same day.