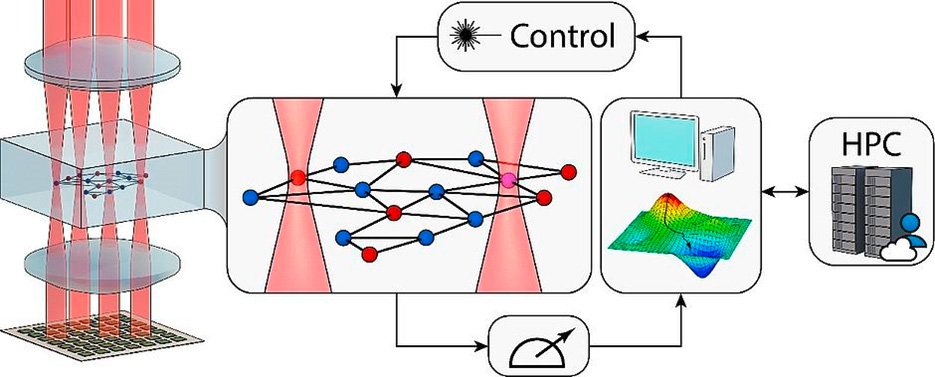
In the project funded by the German Federal Ministry of Research, Technology and Space (BMFTR), we are developing a quantum computing demonstrator based on Rydberg atoms together with our project partners: the Rymax One.
The Rymax consortium is composed of a team of researchers from the University of Hamburg, the RPTU Kaiserslautern and our institute, which has joined forces with leading technology companies. Together, we are pursuing the goal of developing a quantum computer that is capable of solving optimization problems as efficiently as possible – for example, in practical applications in logistics operations, supply chains, and process optimization. Our institute, the Fraunhofer ITWM, forms the bridge between the technology partners, who construct the quantum computer, and the users from Hamburger Hafen Logistik and the OTTO Group, who contribute practical experience.
Together with these associated industrial partners, we identify relevant optimization problems from the logistics environment, which are then to be solved with the help of Rymax One.
Computing With Atoms for Industrial Application
The acronym is made up of the following components: RY stands for Rydberg atoms – one of the ways to realize quantum computing – and MAX describes that the team wants to get the most out of this technology. The quantum computer itself will be located in the newly constructed RPTU research building »Laboratory for Advanced Spin Engineering« (LASE) on the university campus in Kaiserslautern and at the University of Hamburg. Quantum computers have the potential to solve certain mathematical problems better than classical, digital computers. Our task in the project is to appropriately model the practical use cases of the associated inudstry partners and to provide suitable algorithms and software so that we can exploit this potential as well as possible.